Introduction to measles
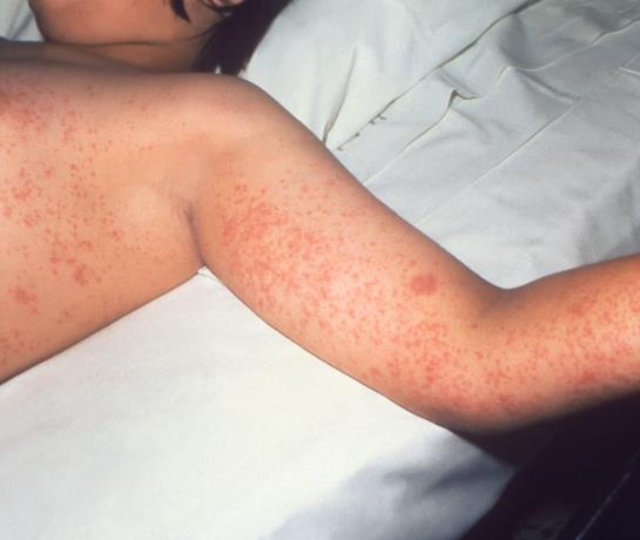
Measles is a highly contagious disease that can have serious complications in some people. It can lead to pneumonia or inflammation of the brain. One in a few thousand people who acquire measles die, with most deaths in unvaccinated or under vaccinated children. Pregnant people who develop measles have an increased risk of serious infection, hospitalization, miscarriage, premature labour, and low birthweight infants.
Measles is spread by an airborne virus when an infected person breathes, coughs or sneezes. You can become infected when you breathe in these droplets. You can also get measles by touching the droplets on an object contaminated with the virus, when you kiss someone, or share food, drinks or cigarettes with an infected person.
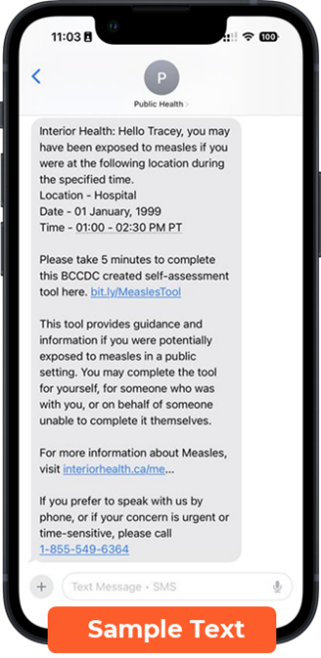
Getting the measles vaccine is the best way to prevent getting and spreading measles. Two doses of a measles-containing vaccine is almost 100 per cent effective and lasts for a lifetime.
Learn more about measles, signs and symptoms, and current cases (BC Centre for Disease Control)