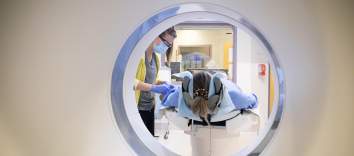
Computed tomography (CT) scans create two-dimensional images of soft tissues and other structures not captured in conventional x-rays. Multiple images, called slices, are usually taken approximately 2.5–5 mm apart. In some cases, 3-D images can be produced depending on the equipment and computer software available.
CT scans are particularly useful in the diagnosis of trauma, musculoskeletal disorders, cardiovascular disease, infectious diseases and cancer.
If you are on a CT scan waitlist, find out more about scheduling your test at a nearby hospital.